What is erectile dysfunction? Managing Erectile Dysfunction with Effective Treatments:
What is erectile dysfunction ?
Erectile Dysfunction (ED), also known as impotence, refers to the inability to achieve or maintain an erection firm enough for satisfactory sexual intercourse. It can be a persistent or recurrent problem, often causing distress and affecting the quality of life for those experiencing it.ED can occur at any age but is more common as men get older, with prevalence increasing with age.
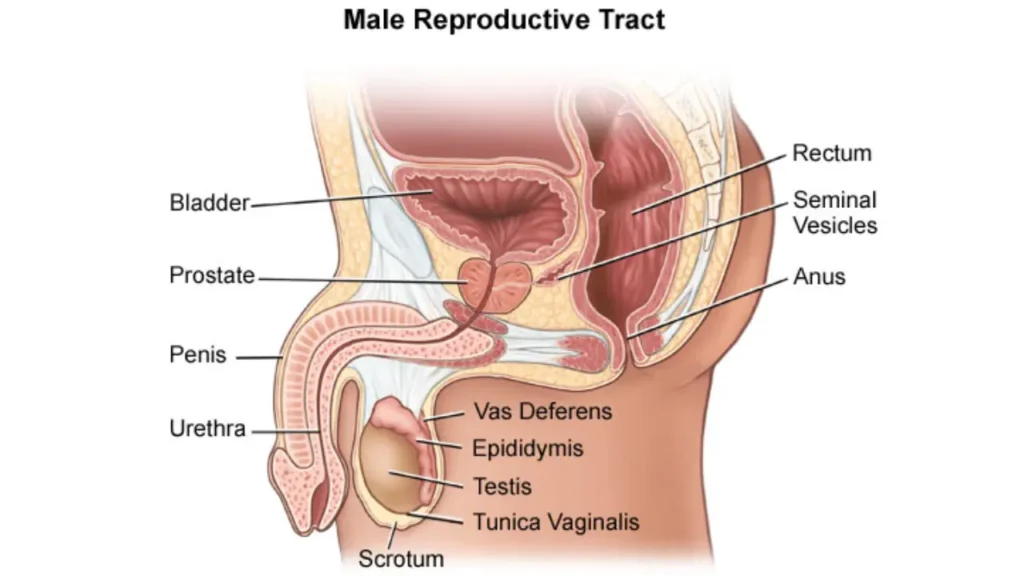
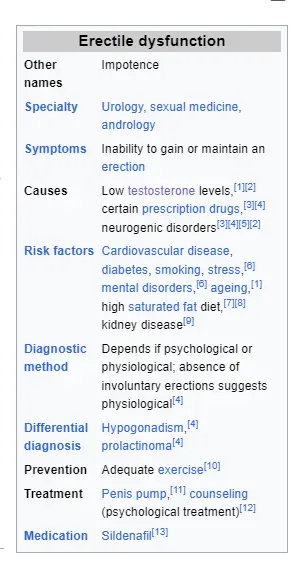
Importance of the Topic
Erectile Dysfunction is a prevalent condition that affects millions of men worldwide, regardless of age, race, or socio-economic status.
It can have significant impacts on personal relationships, self-esteem, and overall well-being, leading to emotional distress and psychological issues.
Understanding ED is crucial for individuals to recognize symptoms, seek appropriate medical care, and explore available treatment options.
Addressing ED is not only essential for improving sexual health but also for promoting overall health and quality of life for affected individuals and their partners.
Erectile Dysfunction Causes
Physical factors
- Chronic diseases: Conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease can damage blood vessels and nerves, leading to erectile dysfunction.
- Neurological disorders: Disorders affecting the nervous system, including multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and spinal cord injuries, can interfere with the transmission of nerve signals to the penis, causing ED.
- Hormonal imbalances: Low levels of testosterone or imbalances in other hormones involved in sexual function can contribute to erectile dysfunction.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as antidepressants, antihypertensives, and prostate cancer treatments, may have side effects that impact erectile function.
- Lifestyle factors: Unhealthy habits like smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, drug abuse, obesity, and lack of physical activity can increase the risk of developing ED by affecting blood flow and overall health. Learn how Shilajit Tackles Erectile Dysfunction
Psychological factors
- Stress and anxiety: Mental stress, performance anxiety, or relationship problems can lead to temporary or persistent erectile dysfunction by interfering with the brain’s ability to send signals to initiate the erection process.
- Depression: Feelings of sadness, hopelessness, or low self-esteem associated with depression can negatively impact sexual desire and arousal, contributing to ED.
- Trauma or past experiences: Previous traumatic sexual experiences, childhood abuse, or relationship conflicts may result in psychological barriers to sexual performance and intimacy.
- Body image issues: Negative perceptions of one’s body, insecurities, or dissatisfaction with physical appearance can affect sexual confidence and contribute to erectile dysfunction.
- Mental health disorders: Conditions such as anxiety disorders, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and bipolar disorder can disrupt normal sexual function and contribute to ED.
Understanding the various physical and psychological factors that can contribute to erectile dysfunction is essential for effective diagnosis and treatment planning. Identifying and addressing underlying causes can help individuals regain sexual function and improve overall quality of life.
Risk Factors for Erectile Dysfunction
Age
- Advancing age is a significant risk factor for erectile dysfunction (ED). As men age, they are more likely to experience changes in hormone levels, reduced blood flow to the penis, and increased prevalence of chronic health conditions that can contribute to ED.
- While ED can occur at any age, studies show that the prevalence of ED increases with age, with a higher incidence among men over 40 and even more so among those over 70.
- Age-related changes in sexual function, such as decreased libido and slower arousal, can also contribute to the higher prevalence of ED in older men.
Medical Conditions
- Chronic diseases: Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, hypertension (high blood pressure), atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), and heart disease, can damage blood vessels and nerves, leading to erectile dysfunction.
- Neurological disorders: Conditions affecting the nervous system, including multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and stroke, can interfere with the transmission of nerve signals involved in the erection process, increasing the risk of ED.
- Hormonal imbalances: Imbalances in hormone levels and deficient testosterone levels can contribute to erectile dysfunction. Conditions such as hypogonadism (low testosterone production) can impact sexual function.
- Prostate conditions: Enlargement of the prostate gland (benign prostatic hyperplasia) or prostate cancer and its treatments can affect erectile function by disrupting nerve pathways or blood flow to the penis. Improve Erectile Dysfunction with Pure Aftabi Salajeet.
Lifestyle Factors
- Smoking: Tobacco use is a significant risk factor for ED, as smoking damages blood vessels and reduces blood flow to the penis, impairing erectile function.
- Excessive alcohol consumption: Chronic alcohol abuse can interfere with hormonal balance, damage the liver, and affect nervous system function, contributing to erectile dysfunction.
- Drug abuse: Recreational drug use, including cocaine, methamphetamine, and opioids, can have adverse effects on sexual function and contribute to ED.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese increases the risk of developing conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and atherosclerosis, which are all associated with erectile dysfunction.
- Sedentary lifestyle: Lack of regular physical activity can contribute to obesity, cardiovascular disease, and other health conditions that increase the risk of ED.
Understanding these risk factors is essential for identifying individuals who may be at higher risk of developing erectile dysfunction and implementing preventive measures and lifestyle changes to reduce the risk or manage the condition effectively.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Erectile Dysfunction
A. Common Symptoms
- Difficulty achieving an erection: The primary symptom of erectile dysfunction (ED) is the inability to achieve or maintain an erection firm enough for satisfactory sexual intercourse.
- Reduced sexual desire: Some men with ED may experience a decrease in libido or interest in sexual activity.
- Soft or incomplete erections: Even if erections are achieved, they may be insufficiently firm for penetration or may not last long enough for satisfactory sexual activity.
- Psychological distress: ED can cause feelings of frustration, embarrassment, anxiety, or depression, especially if it becomes a persistent problem affecting intimate relationships.
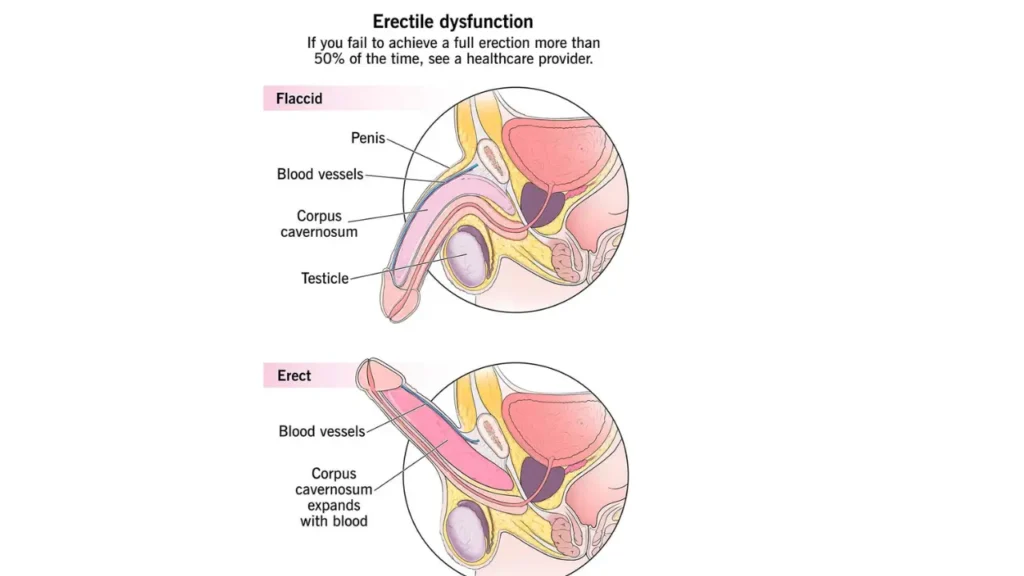
B. Diagnostic Tests
Physical Examination
- Examination of the genitals: A healthcare provider may perform a physical exam to assess the condition of the penis and testicles for any abnormalities, such as Peyronie’s disease (curvature of the penis) or signs of nerve damage.
- Blood pressure measurement: High blood pressure (hypertension) is a risk factor for ED, so checking blood pressure during a physical exam can provide valuable information about cardiovascular health.
Blood Tests
- Hormone levels: Blood tests may be conducted to measure levels of testosterone and other hormones involved in sexual function. Low testosterone levels can contribute to erectile dysfunction.
- Blood sugar levels: Testing for diabetes may be performed since uncontrolled diabetes can damage blood vessels and nerves, leading to ED.
- Lipid profile: High levels of cholesterol and triglycerides can indicate atherosclerosis, which can impair blood flow to the penis and contribute to ED.
Psychological Evaluation
- Interview and questionnaire: A healthcare provider may conduct a thorough interview to assess psychological factors contributing to ED, such as stress, anxiety, depression, or relationship problems.
- Mental health assessment: Screening for underlying mental health disorders or emotional issues that may be affecting sexual function is essential. It may involve evaluating symptoms of depression, anxiety, or other psychological conditions.
- Sexual history: Gathering information about past sexual experiences, current sexual relationships, and any difficulties or concerns related to sexual activity can provide insights into the psychological aspects of ED.
These diagnostic tests help healthcare providers identify the underlying causes of erectile dysfunction and develop an appropriate treatment plan tailored to the individual’s needs. Further, depending on the findings, specialized testing or referrals to other healthcare professionals may be recommended.
Treatment Options for Erectile Dysfunction
A. Lifestyle Changes
- Healthy diet: Adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can improve overall health and erectile function.
- Regular exercise: Regular physical activity, such as aerobic exercises, strength training, and pelvic floor exercises (Kegels), can improve blood flow, boost testosterone levels, and enhance sexual function.
- Weight management: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight reduces the risk of obesity-related conditions like diabetes and cardiovascular disease, which can contribute to erectile dysfunction.
- Smoking cessation: Quitting smoking can improve blood circulation, endothelial function, erectile function, and cardiovascular health.
- Limiting alcohol consumption: Moderating alcohol intake can help prevent alcohol-induced erectile dysfunction and improve sexual performance.
B. Medications
- Oral medications: Phosphodiesterase types 5 (PDE5) inhibitors such as sildenafil (Viagra), tadalafil (Cialis), and vardenafil (Levitra) are commonly prescribed to treat erectile dysfunction by increasing blood flow to the penis and facilitating erections.
- Testosterone replacement therapy: For men with low testosterone levels, hormone replacement therapy may be prescribed to improve libido and erectile function.
- Other medications: In some cases, medications such as alprostadil (Caverject, Edex) or testosterone gel may be used as alternative treatments for ED.
C. Therapy
- Psychological counseling: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), sex therapy, or couples counseling can help address underlying psychological issues contributing to erectile dysfunction, such as performance anxiety, relationship problems, or past trauma.
- Behavioral therapy: Techniques such as sensate focus exercises or systematic desensitization may be used to help individuals overcome psychological barriers to sexual arousal and performance.
- Pelvic floor therapy: Pelvic floor exercises, biofeedback, or electrical stimulation techniques may be recommended to improve erectile function by strengthening the muscles to maintain erections.
D. Surgical Options
- Penile implants: Surgical placement of penile implants, such as inflatable or malleable rods, can provide a permanent solution for erectile dysfunction in men who do not respond to other treatments.
- Vascular surgery: In cases where arterial blockages contribute to erectile dysfunction, surgical procedures such as penile revascularization or arterial bypass surgery may be considered to restore blood flow to the penis.
- Venous ligation: This surgical procedure involves tying off veins to prevent blood from leaving the penis too quickly, thereby maintaining erections for a longer duration.
Treatment options for erectile dysfunction vary depending on the underlying causes, individual health status, and personal preferences. A comprehensive approach that combines lifestyle changes, medications, therapy, and, if necessary, surgical interventions can effectively manage ED and improve sexual function and quality of life.
Psychological Impact of Erectile Dysfunction
A. Effects on Mental Health
- Anxiety: Erectile dysfunction can trigger feelings of anxiety, fear of failure, or performance anxiety related to sexual performance, leading to increased stress levels and emotional distress.
- Depression: Persistent or recurrent ED can contribute to feelings of sadness, hopelessness, or low self-esteem, which may develop into clinical depression if left untreated.
- Self-esteem issues: Erectile dysfunction can negatively impact self-confidence and self-worth, affecting various aspects of a person’s life beyond sexual function.
B. Relationship Issues
- Communication breakdown: Difficulty discussing sexual problems or feelings of inadequacy may lead to communication barriers between partners, causing strain or tension in the relationship.
- Intimacy issues: Erectile dysfunction can disrupt intimacy and closeness between partners, leading to feelings of frustration, rejection, or resentment.
- Changes in sexual dynamics: ED may alter sexual dynamics within a relationship, affecting the frequency of sexual activity, the initiation of intimacy, or the overall satisfaction with the relationship.
C. Coping Strategies
- Open communication: Encouraging open and honest communication between partners about sexual concerns, feelings, and expectations can foster understanding, empathy, and support.
- Seeking professional help: Consulting a therapist, counselor, or sex therapist can provide a safe space to address psychological issues related to ED, learn coping strategies, and improve relationship dynamics.
- Exploring non-sexual intimacy: Engaging in non-sexual activities that promote intimacy, such as cuddling, holding hands, or spending quality time together, can strengthen emotional bonds and maintain closeness.
- Mutual support: Supporting each other through the challenges of erectile dysfunction, acknowledging feelings of frustration or disappointment, and working together to find solutions can strengthen the relationship.
- Stress management techniques: Relaxation techniques, mindfulness, meditation, or yoga can help reduce stress, alleviate anxiety, and improve overall mental well-being.
- Setting realistic expectations: Recognizing that erectile dysfunction is a common and treatable condition and setting realistic expectations for sexual performance can help alleviate pressure and reduce anxiety.
Addressing the psychological impact of erectile dysfunction is crucial for maintaining emotional well-being, preserving relationship harmony, and enhancing the overall quality of life for individuals and their partners. By adopting effective coping strategies and seeking support when needed, individuals can navigate the challenges of ED and maintain fulfilling and satisfying relationships.
Prevention of Erectile Dysfunction
A. Healthy Lifestyle Choices
- Balanced diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support overall health, reduce the risk of obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease, and promote optimal sexual function.
- Regular exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity, such as aerobic exercises, strength training, and pelvic floor exercises, improves blood circulation, enhances cardiovascular health, and reduces the risk of erectile dysfunction.
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Proper diet and exercise can help achieve and maintain a healthy weight, reducing the risk of obesity-related conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and atherosclerosis, which are associated with erectile dysfunction.
- Limiting alcohol consumption: Moderating alcohol intake and avoiding excessive drinking can prevent alcohol-induced erectile dysfunction and maintain sexual health.
- Avoiding tobacco use: Quitting smoking and avoiding tobacco products can improve blood flow, enhance cardiovascular health, and reduce the risk of erectile dysfunction.
B. Regular Medical Check-ups
- Routine physical examinations: Regular visits to a healthcare provider for routine check-ups allow for the early detection and management of chronic diseases, such as diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease, which are risk factors for erectile dysfunction.
- Screening for underlying conditions: Periodic screenings for conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and hormonal imbalances can help identify and address potential contributors to erectile dysfunction.
- Monitoring medications: Regular medical check-ups allow healthcare providers to review and adjust medicines that may have adverse effects on sexual function, such as antidepressants, antihypertensives, and prostate medications.
C. Communication with Healthcare Providers
- Open dialogue: Discussing concerns about sexual health, changes in sexual function, or symptoms of erectile dysfunction with a healthcare provider promotes early intervention and appropriate management.
- Seeking guidance: Seeking guidance from healthcare professionals about lifestyle modifications, preventive measures, and available treatments for erectile dysfunction empowers individuals to take proactive steps to maintain sexual health.
- Compliance with treatment plans: Communicating openly with healthcare providers and adhering to recommended treatment plans, including medications, lifestyle changes, and therapy, can improve outcomes and prevent complications associated with erectile dysfunction.
By adopting healthy lifestyle choices, attending regular medical check-ups, and maintaining open communication with healthcare providers, individuals can reduce their risk of developing erectile dysfunction and promote overall sexual health and well-being. Early detection, prevention, and intervention are crucial to maintaining optimal erectile function and enjoying a satisfying sex life.
Conclusion
Throughout this discussion, we have explored various aspects of erectile dysfunction (ED), including its definition, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, psychological impact, and prevention strategies.
- ED is the inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual performance and can be caused by physical factors, psychological factors, or a combination of both.
- Common symptoms of ED include difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection, reduced sexual desire, and psychological distress.
- Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, blood tests, and psychological evaluation to identify underlying causes and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
- Treatment options for ED include lifestyle changes, medications, therapy, and surgical interventions to improve erectile function and enhance quality of life.
- Psychological effects of ED can include anxiety, depression, and relationship issues, highlighting the importance of addressing the emotional impact of the condition.
- Preventive measures such as healthy lifestyle choices, regular medical check-ups, and open communication with healthcare providers can help reduce the risk of developing ED and promote sexual health and well-being.
B. Importance of Seeking Help
Individuals experiencing erectile dysfunction must seek help from healthcare professionals. Seeking help allows for early diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and effective management of ED, which can significantly improve quality of life and overall well-being.
- Delaying or avoiding seeking help for ED can lead to worsening symptoms, psychological distress, and negative impacts on relationships and self-esteem.
- Healthcare providers are equipped to offer support, guidance, and personalized treatment options tailored to individual needs, addressing both physical and psychological aspects of erectile dysfunction.
- Open communication with healthcare providers fosters a collaborative approach to managing ED, empowering individuals to take proactive steps toward improving sexual health and maintaining fulfilling relationships.
Understanding erectile dysfunction, its causes, and available treatment options is essential for individuals and their partners. By seeking help, addressing underlying issues, and implementing preventive measures, individuals can overcome the challenges of ED and enjoy satisfying sexual experiences and overall well-being.








